1. Model based on Supervised Learning
- Ideal model : \(Y = f(X) + \epsilon\)
- Good \(f(X)\) can make predictions of \(Y\) at new points \(X = x\).
- Statistical Learning refers to a set of approaches for estimating the function \(f(X)\).
# Indexing without index
AD <- Advertising[, -1]
# Multiple linear regression
lm.fit <- lm(sales ~. AD)
summary(lm.fit)
names(lm.fit)
coef(lm.fit)
confint(lm.fit)
# Visualizing models
par(mfrow=c(2,2))
plot(lm.fit)
dev.off()
plot(predict(lm.fit), residual(lm.fit))
plot(predict(lm.fit), rstudent(lm.fit))
plot(hatvalues(lm.fit))
which.max(hat.values(lm.fit))
2. Estimation of \(f\) for Prediction
- \(\hat{Y} = \hat{f}(X)\)
- \(\hat{f}\) : Estimation for \(f\).
- \(\hat{Y}\) : Prediction for \(Y\).
- Ideal function \(f(X)\) is \(f(X) = E(Y|X=x)\).
- Reducible error : \(E[(f(x) - \hat{f}(x))^2]\)
- Irreducible error : \(\epsilon = Y - f(x)\)
- Statistical learning techniques for estimating \(f\) is minimizing reducible error.
- Statistical learning is the way finding \(\hat{f}\) which is the most similar function to \(f\).
3. [Ex] Income Data
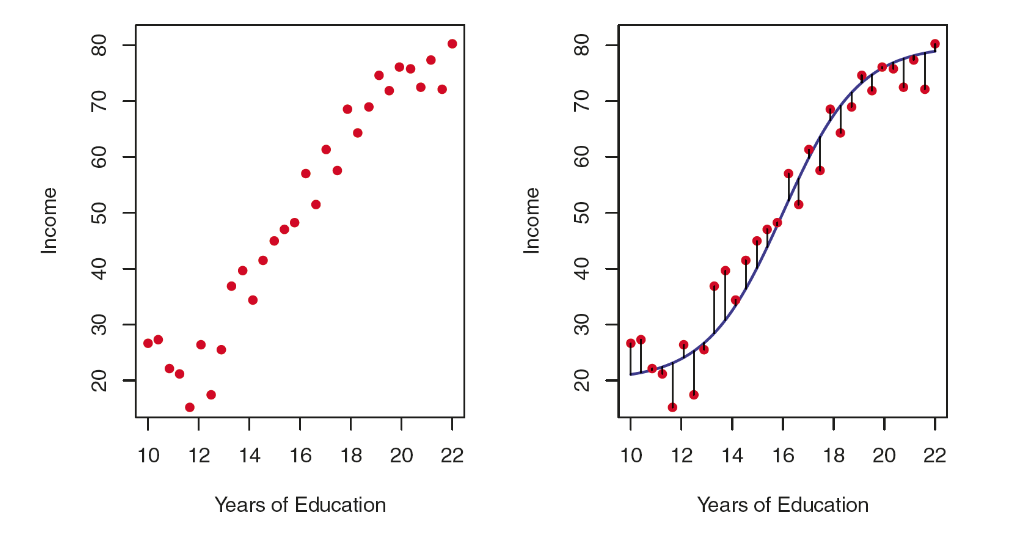
# Load Datasets
url.in <- "https://www.statlearning.com/s/Income1.csv"
Income <- read.csv(url.in, h=T)
# Polynomial regression fit
par(mfrow = c(1,2))
plot(Income~Education, col=2, pch=19, xlab="Years of Education",
ylab="Income", data=Income)
g <- lm(Income ~ ploy(Education, 3), data=Income)
plot(Income~Education, col=2, pch=19, xlab="Years of Education",
ylab="Income", data=Income)
lines(Income$Education, g$fit, col="darkblue", lwd=4, ylab="Income",
xlab="Years of Education")
# Compare residuals
y <- Income$Income
mean((predict(g) - y)^2)
mean(residuals(g)^2)

# Polynomial fit with multiple hyperparameter
dist <- NULL
par(mfrow=c(3,4))
for (k in 1:12) {
g <- lm(Income ~ poly(Education, k), data=Income)
dist[k] <- mean(residual(g)^2)
plot(Income~Education, col=2, pch=19, xlab="Years of Education", ylab="Income",
data=Income, main=paste("k =", k))
lines(Income$Education, g$fit, col="darkblue", lwd=3, ylabe="Income", xlab="Years of Education")
}

x11()
plot(dist, type="b", xlab="Degree of Polynomial",
ylab="Mean squared distance")






